Pakistan’s debt to drop to 63% of GDP by 2028

MG News | November 01, 2025 at 10:45 AM GMT+05:00
November 1, 2025 (MLN): Pakistan’s total public debt is projected to decline from 70.8% of GDP in FY2025 to 63.3% by FY2028, according to the Debt Sustainability Analysis (DSA) Report FY2026–FY2028 released by the Finance Division.
The report paints a cautiously optimistic picture of the country’s fiscal health, noting that while debt remains sustainable under baseline assumptions, it is still vulnerable to shocks from slower growth, exchange rate depreciation, and fiscal slippages.
At the end of June 2025, the country’s total public debt stood at Rs80.52 trillion, up from Rs71.24 trillion a year earlier.
When combined with publicly guaranteed obligations of Rs4.27 trillion, Pakistan’s total public and publicly guaranteed (PPG) debt reached Rs84.79 trillion, equivalent to 74.5% of GDP.
The Finance Division forecasts that the debt ratio will gradually decline over the next three fiscal years, driven by fiscal consolidation, lower interest payments, and stronger economic growth.
“Public debt is projected to remain sustainable over the medium term, supported by macroeconomic stability and prudent fiscal management,” the report states.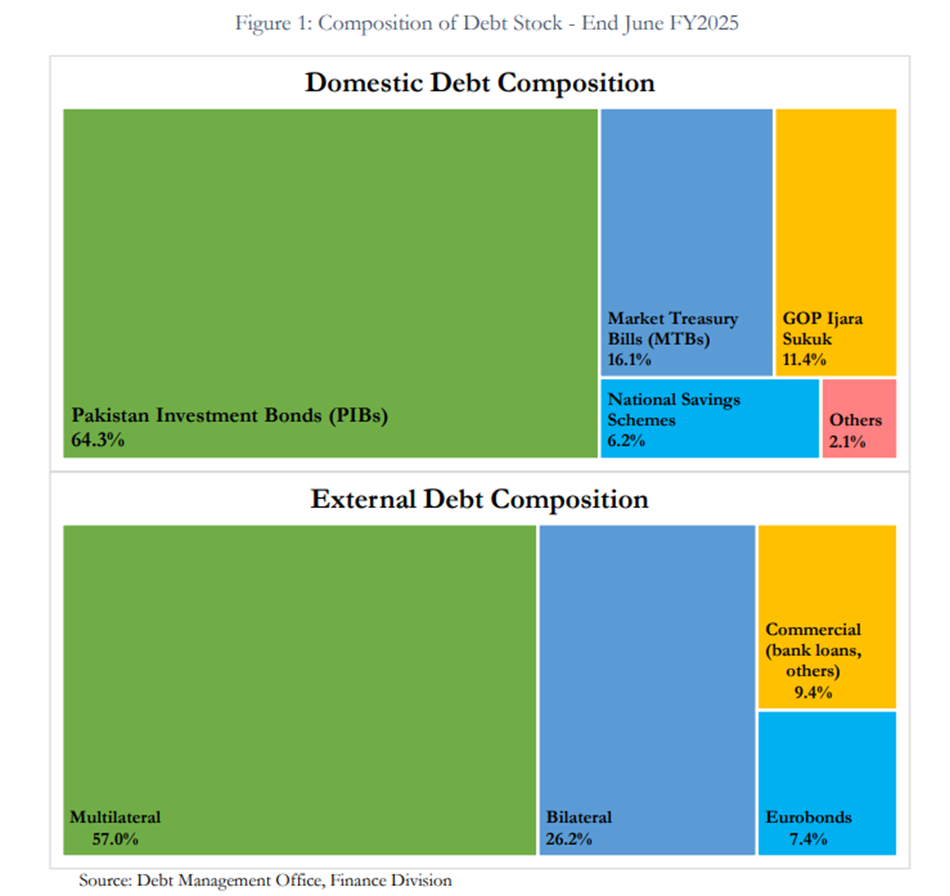
Domestic and External Debt Composition
The report shows that domestic debt accounts for 67.7% of total public debt, with a large portion held in floating-rate instruments, 80% as of June 2025, making it highly sensitive to interest rate fluctuations.
Long-term securities such as Pakistan Investment Bonds (PIBs) and Ijara Sukuks dominate the domestic portfolio.
External debt represents 32.3% of total public debt, largely composed of concessional loans from multilateral and bilateral partners, with an average maturity of over six years.
However, the report flags refinancing risks from the 24% share of short-term external debt and moderate currency risk due to 41% floating-rate exposure.

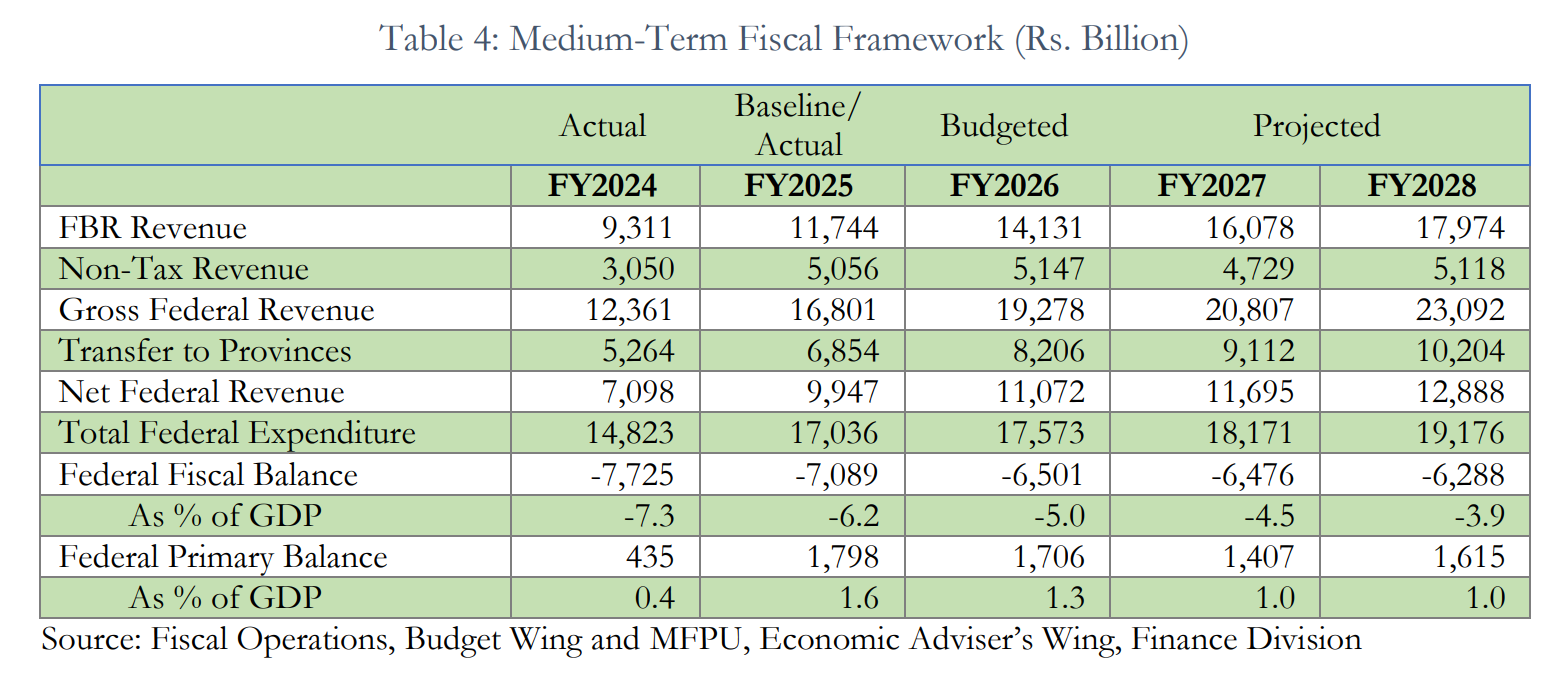
Macroeconomic Stability Restored in FY2025
The DSA attributes the improving debt outlook to a turnaround in FY2025, when Pakistan regained macroeconomic stability after years of high inflation and currency volatility.
Real GDP growth rose to 3%, compared to 2.6% in FY2024, while headline inflation dropped sharply to 4.5% from 23.4% the previous year.
The report credits this improvement to disciplined fiscal management, including reduced markup expenditures, Rs 888 billion in savings, and tighter control on untargeted subsidies.
The federal fiscal deficit narrowed to 6.2% of GDP, outperforming the 6.8% target, and the primary balance posted a surplus of 1.6% of GDP.
“Exchange rate pressures were contained through effective regulation of informal currency markets and cross-border flows,” the report notes, adding that these measures helped improve Pakistan’s sovereign credit ratings and restore access to international markets.
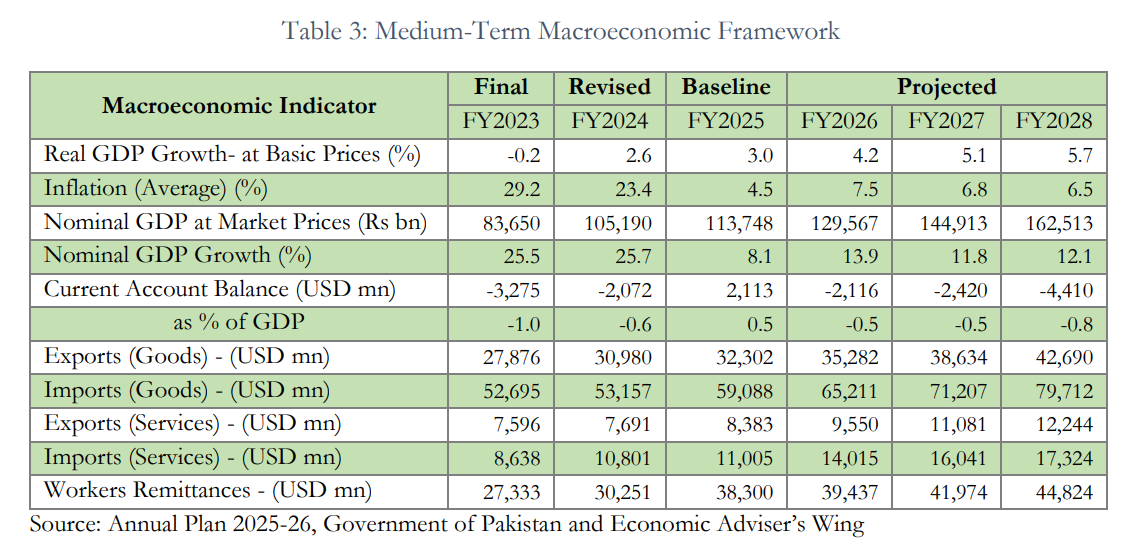
Medium-Term Economic Outlook
According to the DSA’s baseline projections, real GDP growth is expected to rise from 4.2% in FY2026 to 5.7% in FY2028, driven by higher investment and export-led expansion in agriculture, information technology, renewable energy, mining, and pharmaceuticals.
Inflation is forecast to remain moderate between 6.5 and 7.5%, while the exchange rate is projected to stay broadly stable.
The current account, which showed a modest surplus of $2.1 billion in FY2025, is expected to register manageable deficits of under 1% of GDP in subsequent years.
The report emphasizes that improved exports, foreign direct investment, and remittances will help sustain external stability and foreign exchange reserves.
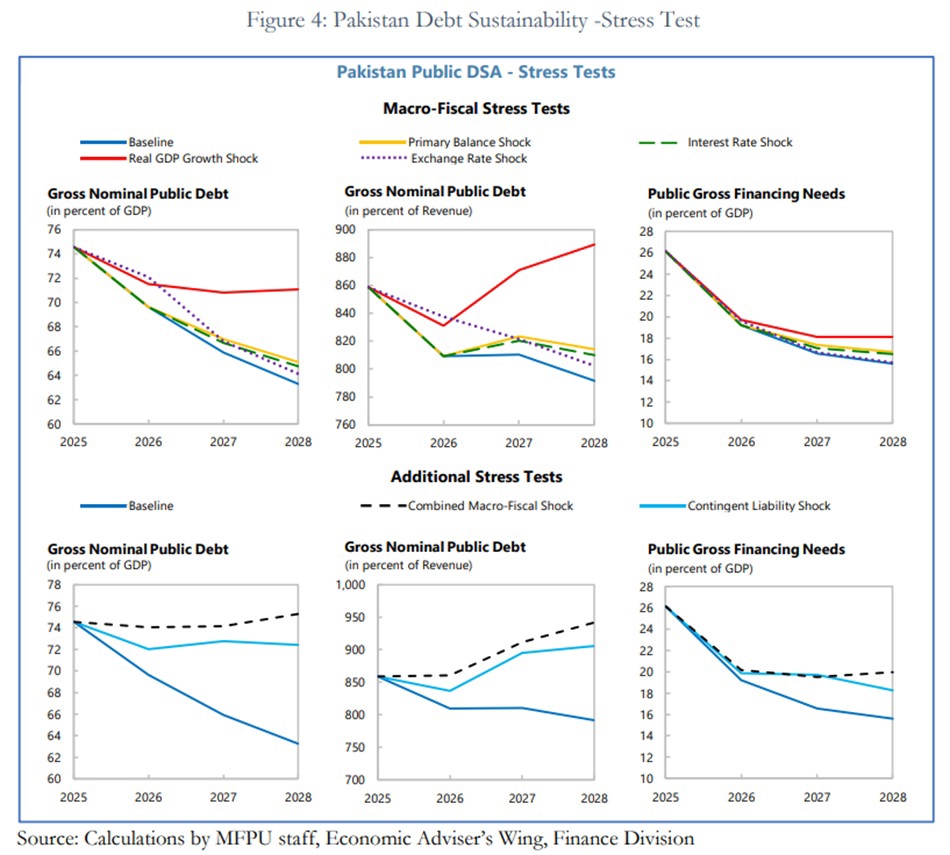
Debt Risks and Stress Scenarios
While the baseline scenario projects a steady decline in debt, the DSA underscores that Pakistan’s debt position remains sensitive to macroeconomic shocks.
Under a series of simulated stress scenarios, debt sustainability weakens if growth slows, interest rates rise, or the rupee depreciates sharply.
If GDP growth falls one standard deviation below baseline for two consecutive years, the PPG debt-to-GDP ratio could rise to 71.1% by FY2028, breaching the sustainability benchmark.
A combined macro-fiscal shock, involving simultaneous hits to growth, fiscal balance, interest rates, and the exchange rate, could push the ratio up to 75.3%, posing a serious risk to fiscal stability.
In contrast, moderate shocks such as higher interest rates or exchange rate depreciation keep debt ratios within manageable limits.
The gross financing needs (GFN) are projected to decline from 26.1% of GDP in FY2025 to 15.6% in FY2028, though this remains slightly above the IMF’s benchmark of 15%.
The government’s medium-term debt strategy focuses on diversifying borrowing sources, extending maturities, and reducing refinancing and interest rate risks.
The Finance Division plans to rely more on concessional borrowing, encourage non-resident investment in government securities, and tap international capital markets under improved credit conditions.
At the same time, fiscal reforms are being implemented to broaden the tax base, digitalize tax administration, and link budget allocations to performance outcomes.
The government also aims to improve expenditure management through targeted subsidies, pension reforms, and right-sizing of government functions.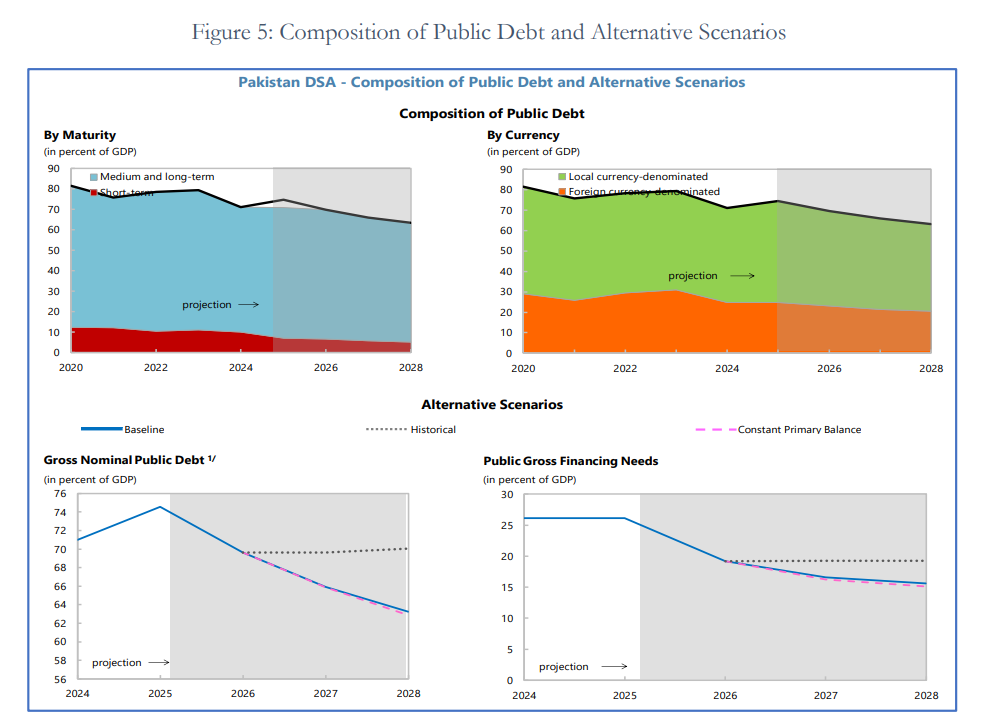
The Debt Sustainability Analysis FY2026–FY2028 concludes that Pakistan’s debt remains sustainable in the medium term but warns that the outlook is fragile under adverse shocks.
The report calls for maintaining fiscal discipline, promoting export-led growth, and enhancing resilience to external pressures.
“Pakistan’s economy achieved stability in FY2025,” wrote Finance Secretary Imdad Ullah Bosal, “and continued reform efforts are vital for safeguarding economic stability and ensuring long-term debt sustainability.”
Copyright Mettis Link News
Related News
| Name | Price/Vol | %Chg/NChg |
|---|---|---|
| KSE100 | 153,866.17 113.04M | -0.36% -555.27 |
| ALLSHR | 92,322.41 289.91M | -0.18% -165.37 |
| KSE30 | 47,054.02 67.50M | -0.57% -268.71 |
| KMI30 | 220,139.18 52.42M | -0.81% -1787.82 |
| KMIALLSHR | 59,630.44 114.87M | -0.43% -258.98 |
| BKTi | 44,089.65 23.49M | -0.09% -38.05 |
| OGTi | 31,668.31 6.28M | -0.15% -47.11 |
| Symbol | Bid/Ask | High/Low |
|---|
| Name | Last | High/Low | Chg/%Chg |
|---|---|---|---|
| BITCOIN FUTURES | 71,495.00 | 74,210.00 70,200.00 | 850.00 1.20% |
| BRENT CRUDE | 103.89 | 103.95 97.60 | 3.43 3.41% |
| RICHARDS BAY COAL MONTHLY | 99.40 | 0.00 0.00 | -12.90 -11.49% |
| ROTTERDAM COAL MONTHLY | 122.70 | 123.80 122.70 | -1.10 -0.89% |
| USD RBD PALM OLEIN | 1,083.50 | 1,083.50 1,083.50 | 0.00 0.00% |
| CRUDE OIL - WTI | 99.31 | 99.32 92.04 | 3.58 3.74% |
| SUGAR #11 WORLD | 14.41 | 14.53 14.30 | 0.03 0.21% |
Chart of the Day
Latest News
Top 5 things to watch in this week
Pakistan Stock Movers
| Name | Last | Chg/%Chg |
|---|
| Name | Last | Chg/%Chg |
|---|

.png?width=280&height=140&format=Webp)
_20251226081441672_22beb3.webp?width=280&height=140&format=Webp)
_20260217183412613_2f8957.webp?width=280&height=140&format=Webp)
 Auto Numbers
Auto Numbers